Remote work has reshaped the way organizations train and develop their teams, pushing companies to rethink their learning strategies. In this context, the Mobile-First LMS in Remote Workforce Training has emerged as a game-changing solution. By placing mobile accessibility at the center of learning design, organizations can ensure that training is flexible, engaging, and inclusive for employees who are scattered across different locations and time zones.
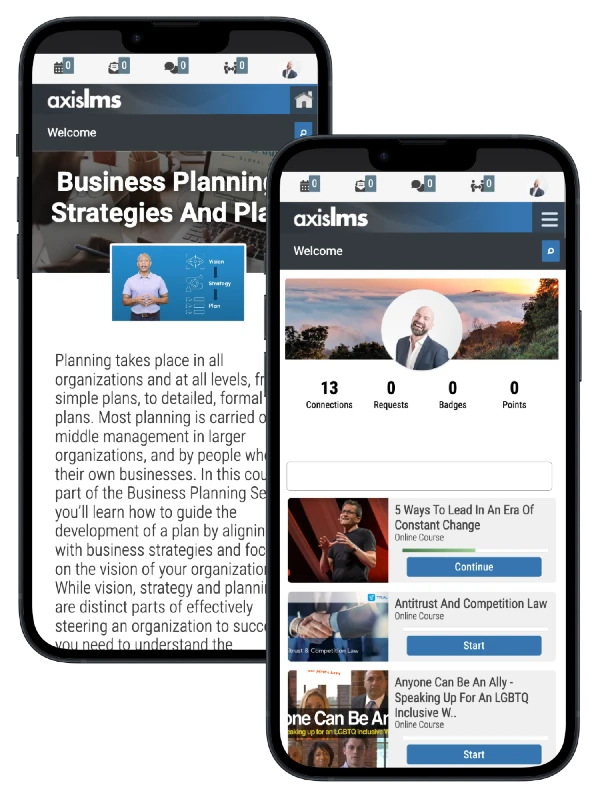
But what does mobile-first really mean in practice, and why is it becoming essential for the modern workforce? This blog dives into these questions and explores the true role of mobile-first platforms in remote employee training.
Why Remote Workforce Training Demands a New Approach
Remote work has become more than just a temporary shift. For many industries, it is now a long-term or even permanent model. The rise of hybrid and fully remote teams has made it increasingly important for organizations to design training systems that are accessible, engaging, and measurable. Traditional methods of learning, such as in-person workshops or desktop-only e-learning modules, often fail to meet the needs of employees who are constantly on the move or working from varied environments.
Remote employees also face unique challenges. They may experience limited access to high-speed internet, juggle multiple time zones, and often struggle with engagement when learning platforms are not user-friendly. A mobile-first learning management system (LMS) offers a solution that addresses these barriers, creating an environment where training is accessible anytime and anywhere.
What is a Mobile-First LMS?
A mobile-first LMS is designed with smartphones and tablets as the primary interface for learning. Unlike platforms that simply adapt to mobile screens, these systems are intentionally developed for mobile use, ensuring optimized navigation, speed, and interactivity.
Key characteristics of mobile-first systems include:
- Responsive design: Training modules fit seamlessly across different devices and screen sizes.
- Microlearning focus: Content is broken into bite-sized modules to suit mobile learning habits.
- Push notifications: Employees receive real-time reminders and updates, keeping them engaged.
This design approach ensures that learners do not feel confined to a desk. Instead, they can train during commutes, while traveling, or whenever they find a pocket of time.
The Benefits of a Mobile-First LMS in Remote Workforce Training
1. Accessibility Across Borders
Remote teams are often spread across multiple countries and regions. A mobile-first LMS ensures that training can reach employees wherever they are. With mobile access, learners no longer need to wait until they are at a desktop computer. Instead, they can log in from any location, turning dead time into productive learning opportunities.
2. Higher Engagement Through Familiar Devices
Most employees already use smartphones extensively for communication, social media, and productivity tools. Training that integrates seamlessly into this daily habit increases adoption and engagement. The learning experience feels less like a separate task and more like an integrated part of the workday.
3. Flexibility for Different Learning Styles
Some employees prefer visual content, while others prefer text or audio. Mobile-first systems often support multiple content types such as video, quizzes, gamified modules, and podcasts. This variety caters to diverse learners and helps organizations achieve higher completion rates.
4. Microlearning for Busy Schedules
One of the strongest advantages of mobile-first platforms is their ability to deliver microlearning. Remote employees often work irregular schedules or juggle multiple tasks. Instead of requiring hours of uninterrupted focus, microlearning delivers knowledge in short bursts that can be completed in minutes.

5. Better Analytics and Insights
Mobile-first systems also improve tracking and reporting. Employers gain insights into how employees interact with training, including when and where they access content. These analytics can help HR and training teams refine their strategies and identify skill gaps faster.
How Mobile-First LMS in Remote Workforce Training Supports Organizational Goals
Beyond improving the learning experience, a mobile-first strategy also contributes to larger business objectives. Organizations that embrace mobile-first training benefit from:
- Faster onboarding: New hires can access resources from day one, even before receiving laptops or desktop access.
- Stronger compliance: Industries that require strict adherence to regulations can deliver compliance training directly to mobile devices, reducing the risk of missed updates.
- Improved retention: Employees who feel supported in their professional development are more likely to stay with the company.
- Scalability: Whether the workforce expands by dozens or thousands, mobile-first systems scale seamlessly without requiring significant infrastructure investments.
The Human Side of Mobile-First Learning
Technology alone does not guarantee success. For mobile-first learning to be effective, organizations must remember the human side of training. Employees want content that feels relevant, personalized, and respectful of their time. Leaders should avoid overwhelming workers with constant notifications or repetitive modules.
Human-centered design means creating learning pathways that align with employees’ goals. For example, giving employees a choice between video-based training or interactive scenarios allows them to learn in ways that feel most natural. Providing opportunities for feedback also strengthens engagement, as employees feel their voices matter.
Addressing Challenges in Mobile-First LMS Adoption
While the benefits are significant, organizations must also be prepared for potential challenges when implementing a mobile-first LMS in remote workforce training.
- Digital fatigue: Constant use of mobile devices can lead to fatigue. Employers should balance training frequency and keep modules concise.
- Data privacy concerns: Mobile training involves storing data across devices. Companies need strong security protocols to protect employee information.
- Connectivity issues: Remote workers in areas with limited internet may struggle to access content. Offline mode can mitigate this problem.
- Generational differences: Some employees may prefer traditional methods over mobile platforms. Providing options ensures inclusivity.
Organizations that anticipate these hurdles and build proactive solutions will see greater success in adoption.
Best Practices for Implementing a Mobile-First LMS
- Conduct a training needs analysis: Understand what skills are most critical for your remote workforce.
- Choose the right platform: Ensure the LMS offers offline functionality, microlearning support, and strong reporting features.
- Design with mobile habits in mind: Keep lessons short, interactive, and optimized for smaller screens.
- Promote inclusivity: Provide accessibility features such as closed captions, screen readers, and multilingual support.
- Measure outcomes regularly: Track progress and gather employee feedback to refine the training strategy.
Industry Applications of Mobile-First LMS
Mobile-first learning platforms are not confined to one sector. Their impact can be seen across industries:
- Healthcare: Training medical staff on compliance protocols through quick, accessible modules.
- Retail: Equipping employees with product knowledge before launches.
- Telecommunications: Delivering technical skill development through specialized modules, where an LMS for telecommunications training provides real-time updates for field workers.
- Small Businesses: Supporting limited teams with cost-effective training solutions, such as an LMS for small companies that does not require heavy infrastructure.
- Large Enterprises: Integrating into broader corporate lms systems that unify training across multiple business units.
Each example demonstrates how mobile-first systems can meet industry-specific challenges while still adhering to broader training principles.
Future Trends in Mobile-First LMS for Remote Training
- AI-driven personalization: Future LMS platforms will analyze user behavior to create individualized training paths.
- Gamification and AR/VR: Immersive technologies will make mobile learning more interactive and engaging.
- Integration with productivity tools: LMS platforms will integrate with project management and communication tools to create a seamless learning ecosystem.
- Enhanced data security: With more mobile use, data encryption and privacy protections will be prioritized.
These trends indicate that mobile-first learning is not a passing trend but a foundational element of the future workplace.
Conclusion
The role of the Mobile-First LMS in Remote Workforce Training is becoming increasingly central as organizations adapt to a more dispersed and digital world. By prioritizing accessibility, flexibility, and engagement, mobile-first platforms empower employees to learn on their own terms. While challenges exist, the benefits of mobile-first training far outweigh the barriers, especially when implemented thoughtfully.
For businesses seeking to strengthen training programs, adopting a mobile-first strategy is not simply a technological upgrade. It is a cultural shift toward inclusivity, adaptability, and forward-thinking workforce development. In the long run, companies that embrace mobile-first solutions will not only train better but will also thrive in the evolving landscape of remote work.